PRECIOUS METALS IN THE FORM OF JEWELLERY, COINS AND BARS
Guide: Hallmark
What is a hallmark?
A hallmark is a mark stamped on items made from precious metals (gold, platinum, palladium, and silver) that are above certain weights. It is a legal requirement to send these items to the Assay Office for hallmarking. A hallmark consists of component marks, such as those applied by the Dublin Assay Office, to guarantee the purity of the precious metal content. A hallmarked item, having been independently tested, certifies the item’s precious metal content. This represents the oldest form of consumer protection and ensures the quality of the precious metal in your purchase.
Why is hallmarking important?
A hallmark is a form of consumer protection, providing information such as the location where the piece was hallmarked, its material composition, and who sent the items for hallmarking. Hallmarks on an item offer detailed information regarding the metal’s purity and fineness. The item is then sent to an Assay Office for testing, before being struck with the relevant hallmark. In Ireland, failure to comply with hallmarking legislation may result in fines or imprisonment.
What do the Symbols of the Full Irish Hallmark Represent?
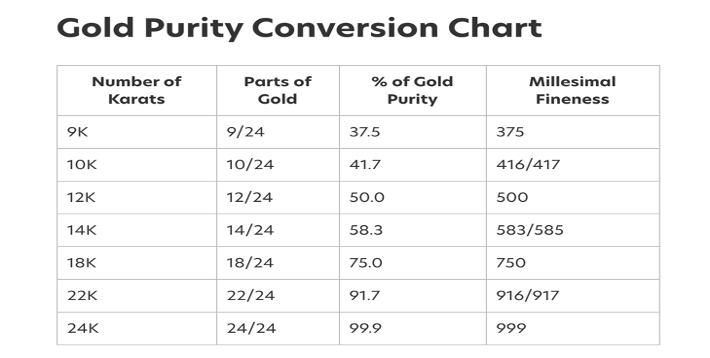
A hallmark provides valuable assurance to customers regarding the purity of precious metal content, measured in parts per 1000. This standard of measurement is recognised in Ireland and other member countries of the International Convention on Hallmarking. For example, 750 parts per 1000 is equivalent to the old 18-karat gold standard.
In Ireland, the Company of Goldsmiths of Dublin which governs the Assay Office located in Dublin Castle, has been testing and certifying gold and platinum jewellery items since 1637.


€

What to Look for in Hallmark Symbols?
Gold, silver, and platinum are the most popular precious metals used in jewellery. You can date and locate a piece of jewellery by using hallmarks. A hallmark is made of three compulsory symbols: the sponsor’s or maker’s mark, the metal and fineness (purity) mark, and the assay office mark.
The Sponsor’s mark
A symbol is used to identify the silversmith or goldsmith, either as an individual or a firm, responsible for making or submitting the items for hallmarking to an assay office.
The Assay Mark
This symbol informs the consumer about where the article was tested. The Hibernia mark, used as a special mark of the Dublin Assay Office, is only applied to items manufactured in Ireland.
The Standard mark
The marks numerically indicate the precious metal’s content, quality, and metal type, all measured in parts per thousand. This mark guarantees that the entire item’s quality is at least equal to the indicated fineness. A 999 mark is equivalent to the standard of 24-karat gold.
The compulsory symbols of Irish hallmark

Sponsor’s Mark, Hibernia Mark, Standard Mark
Figure 1a: The compulsory symbols of 24Karat gold.
Example in figure 1b for 18 Karat gold:
A. Sponsor’s Mark: Sample Sponsor’s Mark
B. Assay Office Mark (Hibernia): used as a special mark of the Dublin Assay Office and only used on Irish manufactured items.
C. The Standard mark: 18Karat Gold, 750 parts per 1000 by weight is equivalent to the old 18 Karat gold standard, The alloy of precious metal must be at least 750 parts per 1000 to be marked as such.
In Ireland, the minimum standard for gold is 9Karat or 375 mark, for platinum 600 mark, palladium 500.

Figure 1b: Sponsor’s mark Hibernia Mark, 18Karat gold purity marks (Source: www.assay.ie)
The Standard Marks
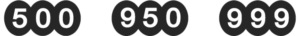


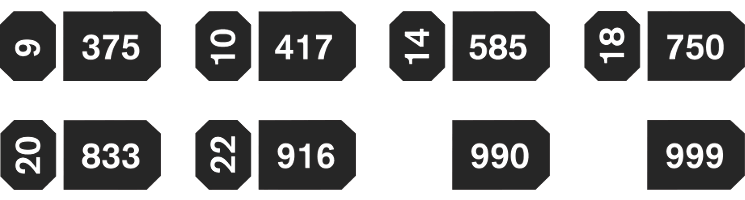
The Optional symbols of Irish hallmark

FIGURE 2: EXAMPLE OF THE OPTIONAL SYMBOLS FOR STERLING SILVER, 18CT GOLD, 20CT GOLD, 22CT GOLD(SOURCE: ASSAY.IE)
Date Letter
Alphabets mark are invaluable in helping you to figure out where a piece of antique jewellery has come from, and how long it’s been around. Each of alphabets mark on any item, demonstrating their authenticity and heritage, so it is easier to date.
If you would like to learn more about the optional symbols of Irish hallmark.
The Date Letter

The Common Control and Convention Marks
The “Hallmarking Convention”, the “Vienna Convention” or the “Precious Metals Convention” was signed in Vienna in November 1972. The Convention Marks on the Control and Marking of items of Precious Metals is an international treaty between States on the cross border trade in precious metal articles and maintaining consumer protection. The scope of the Convention is strictly limited to the control of the precious metal content, not for health, security or other aspects of precious metals articles.
The Members of the Convention are Austria (1975), Sweden (1975), Switzerland (1975), Finland (1975) the United Kingdom (1976), Ireland (1983), Czech Republic (1994), Portugal (1982), Norway (1983), Denmark (1988), Netherlands (1999), Greenland (2004) Latvia (2004), Lithuania (2004), Israel (2005), Poland (2005), Hungary (2006), Cyprus (2007), Slovak Republic (2007), Slovenia (2009), and Croatia (2018).
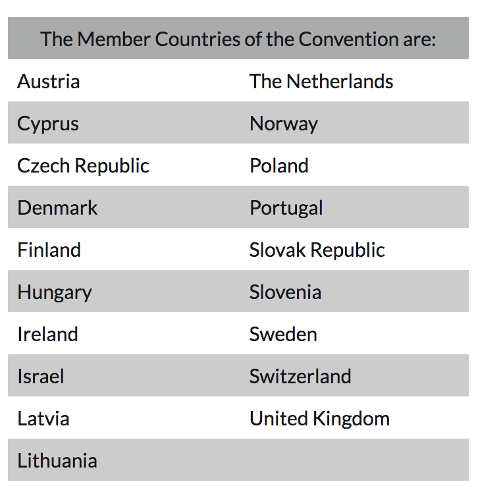
Figure 4: The member of International Convention Marks (Source: Assay. ie)
JOIN RUBYTA
Join Rubyta today and experience bullion in the form of jewellery and accessories. By signing-up our newsletters, you may be the first to know about exciting new designs, special events, store openings and much more.